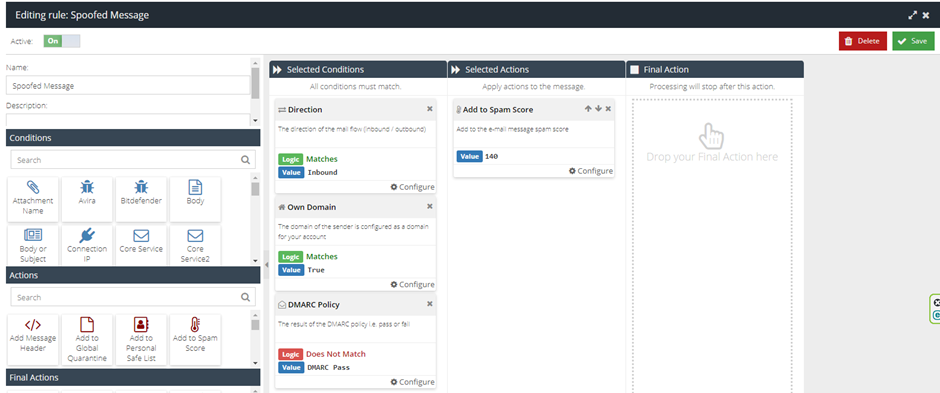
Identifying Spoofed Emails
The Spoofed Emails rule relies on DMARC and SPF records to match the domain they are being received by. It also relies on the Account to be configured properly, as it relies on the following KB articles:
It is very important to first of all, verify the issue is present in Analytics, by finding the email, opening More Details and going to the Actions Tab. You can then export the Server Log/Headers if you need to further verify that there is a difference between the Sender domain and the FROM address of an email.
If an email appears to be sent from: support@censornet.com
But the actual sender address is: mail123421.awsemails.net
These emails would be caught by the Spoofed Messages rule, as it looks at matching your Own Domain:
Censornet.com
But fails the DMARC policy as its not a listed entry in the DMARC or SPF text file.
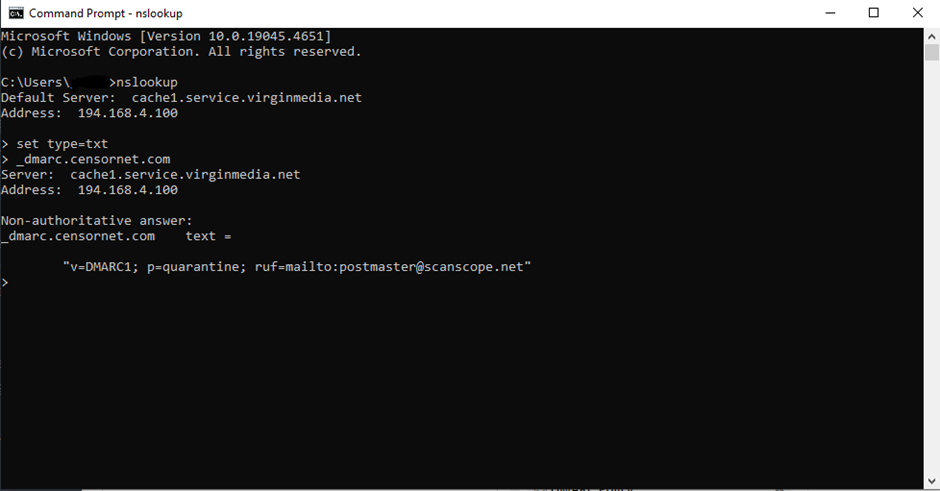
To further understand if a domain has the correct configurations in their DMARC record you can do the following: Open up windows command prompt and type the following and hit enter:
nslookup
the type and hit enter again:
set type=txt
you can then search the dmarc record for any domain by using typing it in the following format:
_dmarc.domain.com
The full output should look something like this if the domain has DMARC ser up:
To then check the SPF record of a domain you can do this following similar steps to the previous section:
type the following and hit enter:
nslookup
the type and hit enter again:
set type=txt
Then search the domain, without the dmarc prefix:
domain.com
Once again, the output should look like this:
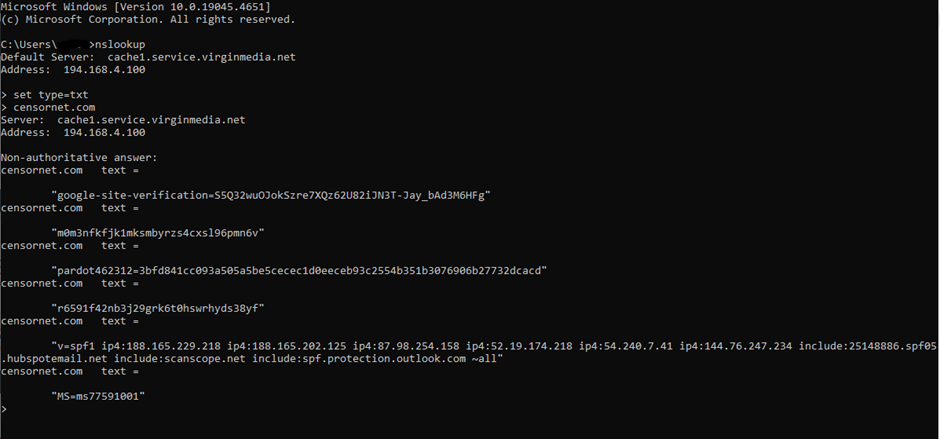
so what we are looking for is verifying that the sending server matches what's listed on the SPF reconrd in the section which starts with "v=spf1", the sender is not on that list it is considered and SPF fail. The spoof message rule will trigger if dmarc does not pass and the sender does not match SPF.